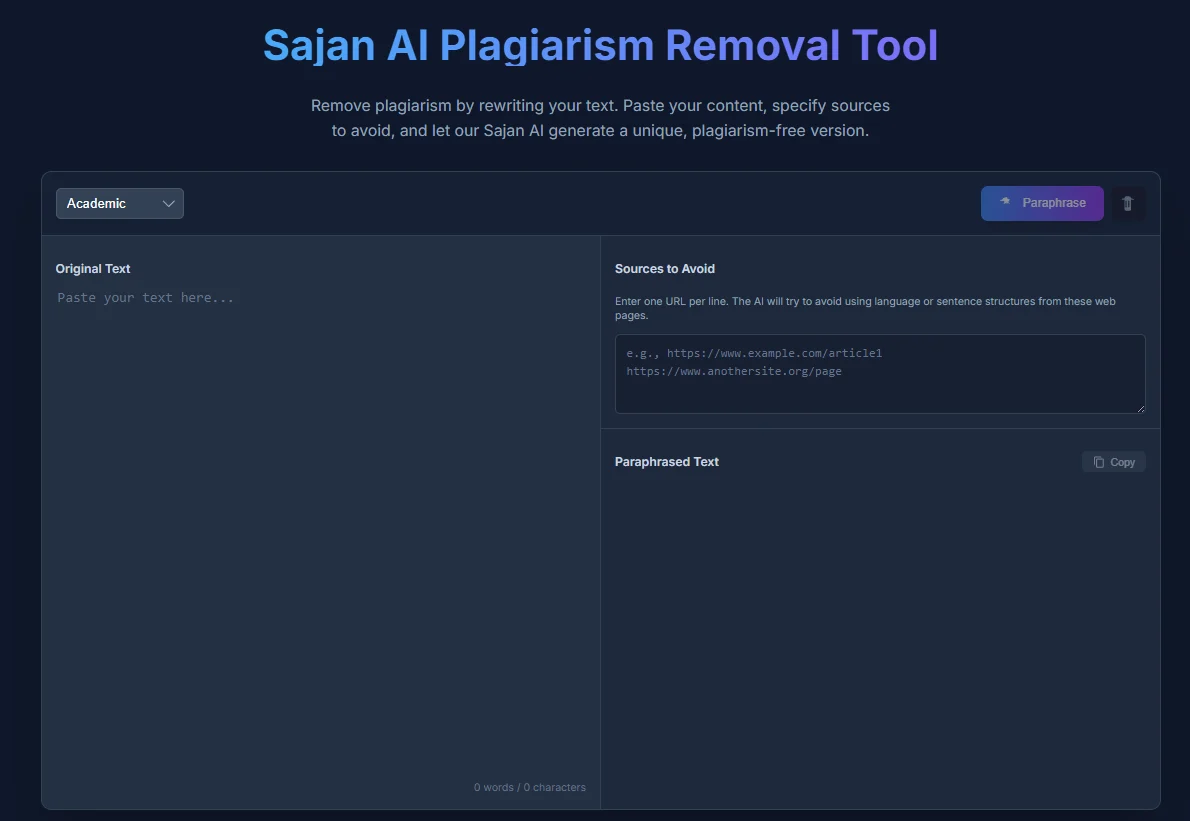
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Plagiarism in Academic Writing
Plagiarism, a term derived from the Latin word “plagiarius,” meaning “kidnapper,” refers to the act of using someone else’s work, ideas, or intellectual property without proper attribution, thereby presenting them as one’s own. In academic writing, where originality and integrity are paramount, plagiarism is considered a serious offense that undermines the credibility of the writer and the institution they represent. It not only violates ethical standards but also hampers the progress of knowledge by preventing the rightful acknowledgment of creators and thinkers.
Within the realm of thesis and article writing, various forms of plagiarism can manifest. These include direct plagiarism, where a writer copies someone else’s text verbatim without quoting, and self-plagiarism, where an author reuses their previous work without appropriate citation. Additionally, mosaic plagiarism occurs when a writer takes phrases from multiple sources and arranges them into a new format without giving credit. Lastly, paraphrasing plagiarism involves inadequately rephrasing someone else’s ideas while failing to provide accurate citations. Each of these forms reflects a lack of scholarly rigor and respect for original thought.
The significance of addressing plagiarism is critical, particularly in academic and research contexts. Not only can incidents of plagiarism lead to severe academic penalties, including expulsion or revocation of degrees, but they also damage a scholar’s reputation and professional relationships. In an era where information is abundant and easily accessible, upholding ethical writing practices is essential for maintaining the integrity of academic work. Consequently, fostering an environment that prioritizes originality and accountability is vital for educators, students, and researchers alike, ensuring that contributions to knowledge are both recognized and respected.
Importance of Proper Referencing
Accurate sourcing and referencing are pivotal aspects of academic integrity in thesis and article writing. Proper referencing not only enhances the credibility of the work, but it also allows readers to trace the origin of ideas and arguments. In the context of academic writing, proper acknowledgment of the original source material is a fundamental practice that upholds intellectual honesty and respect for the contributions of other scholars.
Organizations such as the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), and the Chicago Manual of Style provide structured guidelines for citing sources consistently. Each referencing style has its own unique requirements regarding formatting citations and bibliographies, emphasizing the necessity for authors to familiarize themselves with these different formats. For example, APA style focuses on the author-date format, which highlights the relevance of the publication date, whereas MLA emphasizes the author’s name and the page number in in-text citations. Understanding these nuances helps ensure that references are not only accurate but also formatted correctly for academic submission.
Failure to reference sources properly can lead to significant consequences, including allegations of plagiarism, which is a serious offense in academia. Ignoring the necessity of proper sourcing can damage a scholar’s reputation and undermine the credibility of their research. Moreover, it could result in academic penalties, such as failing grades or even expulsion from educational institutions. By employing consistent referencing practices, writers can safeguard themselves against unintentional plagiarism and contribute effectively to scholarly discourse. It is essential for authors to invest time in learning about the different citation formats and their appropriate applications to strengthen the rigor of their writing and uphold academic standards.
Using Quotation Marks Correctly
Quotation marks play a pivotal role in academic writing, particularly in thesis and article creation, where clarity and integrity of sources are paramount. They are utilized to indicate direct quotes, definitions, and phrases that are universally accepted. Understanding how to effectively employ quotation marks not only acknowledges the original author but also enhances the credibility of your work.
Direct quotes are the most common application of quotation marks. When you incorporate the exact words from a source, it is crucial to enclose them in quotation marks. For instance, if a text states, “The research indicates a significant correlation between variables,” presenting it as such maintains fidelity to the original context. It is equally important to accompany any quoted material with proper citations, offering clear reference to the source and allowing readers to track the information back to its origin.
In addition to direct quotes, quotation marks can be used for defining terms that may not be universally understood. Introducing a specific terminology with its definition, such as “interdisciplinary studies” meaning the integration of methods from various academic fields, requires quotation marks to denote the uniqueness of the term. This practice helps establish a clear understanding for readers unfamiliar with specialized language.
Moreover, when discussing widely accepted phrases or sayings, quotation marks serve to differentiate between your ideas and those established by others. For example, phrases like “the butterfly effect” highlight concepts recognized across the scholarly community. Properly using quotation marks ensures that you respect intellectual property and contribute to academic rigor. Integrating quotations seamlessly into your writing not only maintains the original integrity of sources but also bolsters your arguments, providing robust support while avoiding plagiarism.
Conducting Early Plagiarism Checks
In the academic landscape, maintaining originality in thesis and article writing is imperative. One of the most effective measures to ensure this is conducting early plagiarism checks. Engaging in similarity checks during the initial stages of writing not only helps in identifying potential issues with content overlap or duplication but also provides writers with the opportunity to make necessary adjustments before the final submission. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unintentional plagiarism and enhances the overall quality of the work.
Numerous plagiarism detection tools and software are available to assist writers in evaluating the originality of their content. Popular tools such as Turnitin, Grammarly, and Copyscape stand out for their robust features, allowing users to scan documents against extensive databases and the internet. These platforms provide detailed reports highlighting similarities with existing texts. For optimal effectiveness, it is advisable to familiarize oneself with the functionalities of the chosen tool, understanding how to interpret the results accurately. Setting a clear workflow where one conducts multiple checks throughout the writing process encourages ongoing awareness of content originality.
To perform a thorough similarity check, writers should upload their drafts into the selected plagiarism detection software. It is advisable to run these checks at various milestones of the writing process rather than waiting until the manuscript is fully complete. Early checks can catch inadvertent similarities in ideas or phrases, enabling authors to rephrase, paraphrase, and appropriately attribute sources as necessary. Furthermore, a careful reading of the flagged content aids in recognizing potential areas requiring further scrutiny. By prioritizing early plagiarism checks, writers foster a habit of academic integrity, thereby ensuring their contributions to scholarship remain both unique and credible.
Effective Paraphrasing Techniques
Paraphrasing is a vital skill in academic writing, particularly in thesis and article composition. It involves restating the ideas of an original text in one’s own words while maintaining the original meaning. This not only helps in mitigating plagiarism but also fosters a deeper understanding of the material. A proficient paraphrase should capture the essence of the primary text and adapt its language to reflect the writer’s unique voice.
One effective technique for paraphrasing is to thoroughly comprehend the original text. Reading it multiple times enables the writer to grasp the underlying concepts and intentions. After understanding, one might jot down key points or ideas without looking at the source. This approach encourages the writer to internalize the content and reframe it authentically.
Another useful strategy is the use of synonyms and varied sentence structures. Instead of merely substituting words, a writer can change the sentence format—transforming passive voice into active voice, for instance. Consider the original sentence: “The results were analyzed by the researchers.” A paraphrase could be, “The researchers analyzed the results.” This method preserves the core idea while altering the phrasing.
Moreover, it is beneficial to break down complex sentences into simpler ones. For example, the sentence “Despite the challenges faced, the team completed the project ahead of schedule” could be paraphrased as “The team finished the project early, even though they encountered difficulties.” This not only simplifies the expression but also enhances clarity.
To conclude, effective paraphrasing is an essential tool for writers, promoting originality and a better understanding of material. By applying techniques such as understanding context, using diverse vocabulary, and reworking sentence structures, one can create paraphrases that are both meaningful and distinct, reducing the risk of plagiarism in academic work.
Consulting Your Supervisor Regularly
Consulting your supervisor regularly is a critical aspect of the academic writing process, particularly in the context of thesis and article writing. Engaging with a supervisor or mentor can significantly enhance the quality of your work while simultaneously minimizing the risk of unintentional plagiarism. Regular discussions allow for an exchange of ideas, ensuring that your writing remains original and correctly cited.
One of the primary benefits of frequent consultations is the opportunity for constructive feedback on drafts. When you share your work with your supervisor, you receive valuable insights that can help clarify your thoughts, limit ambiguities, and guide your research direction. This ongoing dialogue fosters an environment of critical thinking and encourages you to articulate your ideas more clearly, thereby reducing the chances of incorporating content that might resemble others’ work too closely.
Moreover, supervisors often have a wealth of experience in recognizing and mitigating plagiarism. They can help you identify areas where improper citation may occur and suggest more effective strategies for paraphrasing or presenting ideas that are inspired by other authors. By relying on their expertise, you can refine your writing style and better understand the ethical standards associated with academic contributions.
In addition to offering guidance on your writing, regular consultations create an opportunity to discuss your research methodologies and sources. By verifying the resources you intend to use early on, you can ensure that they are correctly referenced and that you are sufficiently distanced from any potentially plagiaristic material. This proactive approach not only fosters originality in your work but also instills a sense of accountability in maintaining academic integrity throughout the writing process.
Summarizing Literature Reviews Concisely
In the realm of thesis and article writing, literature reviews serve a foundational role by situating research within the existing body of knowledge. It is crucial to summarize these reviews concisely, distilling key findings from multiple sources into a coherent narrative. This approach not only fosters clarity for the reader but also upholds academic integrity by ensuring that appropriate credit is given to the original authors. Effective summaries can provide significant insights while avoiding redundancy, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the scholarly work.
To achieve a concise summary, writers should engage in critical reading and analysis of the sources they intend to incorporate. This involves identifying the primary arguments, methodologies, and findings of each relevant work. Once these elements are extracted, the next step is to synthesize them into a unified framework that highlights the relationships between different studies. A well-structured literature review is one that captures the essence of each source without overwhelming the reader with excessive detail. By presenting findings succinctly, it becomes easier to both understand and follow the progression of research themes.
Additionally, maintaining a neutral tone is paramount in literature reviews. Writers should ensure that their personal opinions do not overshadow the findings of the cited works. This can be achieved by employing paraphrasing effectively, allowing for original ideas to be conveyed in one’s own words while still honoring the core messages of the original authors. By doing so, the risks of plagiarism can be significantly mitigated, as the reliance on direct quotes can lead to unintentional duplication of text. Furthermore, integrating citations correctly bolsters credibility and supports the ethical standards of academic writing.
Creating a Plagiarism Prevention Strategy
Developing a robust plagiarism prevention strategy is essential for any writer, particularly those engaged in thesis and article writing. A well-structured approach helps in maintaining integrity and originality, which are paramount in academia and professional settings. To begin crafting this strategy, it is crucial to cultivate good writing habits from the inception of the project.
First and foremost, establishing a clear understanding of what constitutes plagiarism is vital. This involves recognizing different forms of plagiarism, whether direct copying, paraphrasing without credit, or inappropriate citation. Familiarizing oneself with various citation styles, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, enhances the ability to accurately attribute sources. Creating a personal checklist incorporating these citation standards can serve as a valuable reference throughout the writing process.
Next, maintaining organized notes is a critical measure. As you conduct research, record not only relevant information but also details of the original sources, including authors, titles, publication dates, and page numbers. Utilize digital tools or apps for source management that facilitate easy organization and retrieval of this data. Additionally, incorporating a consistent process for labeling and saving files can aid in avoiding confusion, thus supporting original thought production.
Another important aspect of a plagiarism prevention strategy is to promote the practice of drafting and revising. Writing a first draft without worrying excessively about perfection allows for the organic flow of ideas, but it is crucial to revisit these drafts to ensure that all ideas are adequately cited. Engaging peers or using writing centers for feedback can also provide new perspectives and help identify areas where more citations may be needed.
Lastly, utilizing plagiarism detection software prior to submission is a practical step to safeguard against unintentional errors. These tools assist in identifying similarities with existing works and help refine the final document. By adhering to these strategies, writers can enhance their originality and uphold the highest academic standards.
Conclusion: Upholding Academic Integrity
In the landscape of academic writing, the importance of upholding integrity cannot be overstated. Throughout this discourse, we have examined various effective measures aimed at reducing plagiarism in thesis and article writing. These methods, ranging from rigorous citation practices to the implementation of advanced plagiarism detection tools, contribute substantially to the cultivation of an environment that fosters original thought and respect for intellectual property.
First and foremost, it is imperative for scholars and authors to recognize their ethical responsibility in producing original content. Engaging with source materials should not merely be about extracting information but involves a deeper understanding and critical engagement with existing literature. By doing so, researchers not only contribute to the elevation of academic standards but also enhance their credibility within their fields. We discussed the necessity of proper attribution which is fundamental in acknowledging the work of others, thus reinforcing the foundation of academic discourse.
Moreover, educational institutions have a pivotal role in instilling the values of academic integrity early in the writing process. This includes providing comprehensive training on ethical writing practices and familiarizing students with the tools and techniques available to check for plagiarism. Such initiatives not only benefit the individual writer but also protect the collective reputation of the academic community.
Ultimately, the promotion of original writing goes hand in hand with respect for the contributions of others, ensuring that scholarly work remains robust, credible, and trustworthy. By embracing the principles of ethical writing and committing to the standards of academic integrity, both emerging and seasoned authors can contribute positively to the scholarly community and the advancement of knowledge.